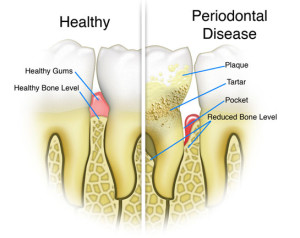
Periodontal diseases are severe infections of the gum tissue which surround teeth. The symptoms of gum diseases can vary from slight bleeding and swelling of gum tissue, to bone destruction and tooth loss. While there are many factors that can contribute to the development of periodontal disease, it is important to practice good oral hygiene to prevent gum disease.
Common Types of Periodontal Disease:
Gingivitis – Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease which is also the least severe and is reversible through special cleaning procedures and personal care. Gingivitis is identified by swollen gums which bleed. When left untreated, gingivitis will likely lead to a more severe condition known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis – Periodontitis is a condition where the bacteria in plaque spreads from the tooth surface to below the gum line causing damage to gum and bone tissue which can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Gum tissue begins to detach from the teeth, allowing bacteria to grow in areas where it can’t be removed by home oral hygiene. Special cleaning procedures need to be done by a periodontist to reverse the damage done by the bacteria to allow gum tissue to reattach to the teeth.
Forms of Periodontitis:
Aggressive Periodontitis – Rapid destruction of gum and bone tissue because of aggressive bacteria with no causes linked to other health conditions.
Chronic Periodontitis – Slow and steady destruction of gum and bone tissue.
Always visit your dentist for regular checkups to help avoid and diagnose periodontal diseases. Quick detection allows prompt treatment to reverse the damage caused by bacteria.